python upsampling, downsampling
time seires data를 분석할 때 불규칙적으로 수집되는 데이터의 특성상 주기가 다소 불규칙적일 때가 많아서 주기를 일정하게 변경해야할 필요성이 있다. 불규칙 적인 time seires data를 주기가 일정하게 변경하는 방법은 upsampling, downsampling 두가지가 있다.
python에서는 pandas 라이브러리의 resample 함수를 활용하여 쉽게 upsampling, downsampling 할 수 있다.
언제 다운 샘플링과 업샘플링을 할까?
(1) 다운샘플링 : 데이터의 빈도를 줄이는 것
- 원본 데이터의 시간 단위가 실용적이지 않은 경우
- 특정 주기에 집중하는 경우
- 더 낮은 빈도의 데이터에 맞추는 경우
3가지로 나누어 설명했지만, 수집 된 데이터가 우리가 핸들링 하기에 적당하지 않은 경우 초 -> 분, 분 -> 시 등으로 더 높은 차원의 시간 대로 resampling 한다고 생각하면 된다.
# create data
index = pd.date_range('1/1/2000', periods=9, freq='T')
series = pd.Series(range(9), index=index)
series
# resamling 3T
series.resample('3T').sum()
- 00:00:00 0<= x < 3
- 00:00:03 3<= x < 6
- 00:00:06 6<= x < 9
각 시간 별로 수집 된 데이터는 위의 수식을 참고하면 쉽게 이해 할 수 있다.
# resamling 3T( label = 'right')
series.resample('3T', label='right').sum()
- 00:00:03 0<= x < 3
- 00:00:06 3<= x < 6
- 00:00:09 6<= x < 9
# resamling 3T( label = 'right', closed='right)
series.resample('3T', label='right', closed='right').sum()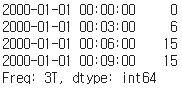
- 00:00:00 x <= 0
- 00:00:03 0 < x <= 3
- 00:00:06 3 < x <= 6
- 00:00:09 6 < x <= 9
(2) 업샘플링 : 실제 데이터를 바탕으로 더 조밀한 시간의 데이터를 얻기 위해 데이터를 생성하는 것
- 시계열이 불규칙적인 상황
- 입력이 서로 다른 빈도로 샘플링 된 상황
업샘플링은 다운샘플링과 반대로 분 -> 초 , 5초 -> 1초 와 같이 더 높은 시간의 단위에서 더 조밀한 시간 데이터를 얻을 수 있다.
# create data
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
rng = pd.date_range('2019-12-31', periods=3, freq='5S')
ts = pd.DataFrame(np.array([0, 1, 3, 2, 10, 3]).reshape(3, 2),
index=rng,
columns=['col_1', 'col_2'])
ts
ts_upsample = ts.resample('S').mean()
ts_upsample
# 앞의 값으로 뒤의 값 채우기
ts_upsample.ffill()
ts_upsample.fillna(method='ffill')
ts_upsample.fillna(method='pad')

# 뒤의 값으로 앞의 값 채우기
ts_upsample.bfill()
ts_upsample.fillna(method='bfill')
ts_upsample.fillna(method='backfill')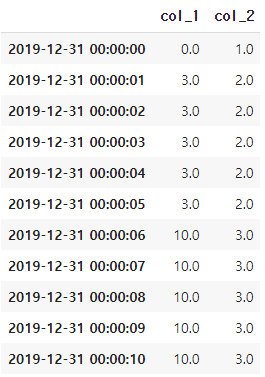
# 선형보간
ts_upsample.interpolate(method='values')
ts_upsample.interpolate(method='time')
자료 생성은 아래의 두 링크를 참고했다.
https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/reference/api/pandas.DataFrame.resample.html